The exchange rate between the United States Dollar (USD) and the Russian Ruble (RUB) is a critical aspect of international finance that influences global trade, investment, and economic stability. This article aims to explore the factors affecting the USD to RUB exchange rate, the historical trends, and the potential implications for various stakeholders.
Table of Contents
ToggleHistorical Overview:
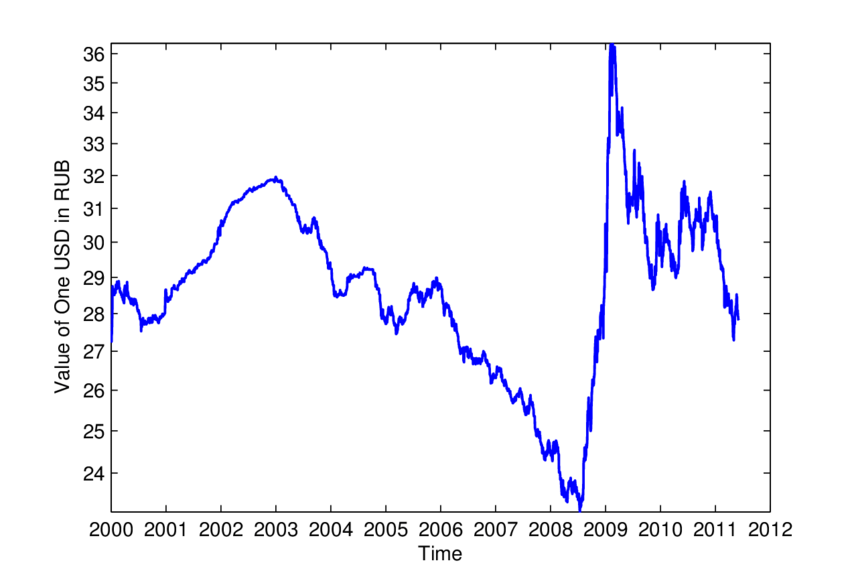
The history of the USD to RUB exchange rate has been marked by volatility, influenced by geopolitical events, economic policies, and global market dynamics. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the introduction of the Russian Ruble as an independent currency. In the subsequent years, Russia faced economic challenges, including hyperinflation and financial instability.
During the 1998 Russian financial crisis, the RUB experienced a significant depreciation against the USD, leading to a period of economic turmoil. In the early 2000s, as Russia implemented economic reforms and stabilized its financial system, the RUB regained strength against the USD.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates:
- Economic Indicators: Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment data, play a crucial role in determining exchange rates. Positive economic performance in either the U.S. or Russia can strengthen their respective currencies.
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, which affect currency values. Higher interest rates in the U.S. can attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the USD relative to the RUB.
- Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events, such as sanctions, political instability, or conflicts, can significantly impact exchange rates. For instance, sanctions imposed on Russia by the U.S. and its allies have historically affected the RUB.
- Trade Balances: The trade balance between two countries influences their exchange rates. If a country has a trade surplus (exports exceed imports), its currency may strengthen. Conversely, a trade deficit can lead to a weaker currency.
- Global Commodity Prices: Russia is a major exporter of commodities, especially oil and gas. Fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly oil, can impact the Russian economy and subsequently affect the RUB exchange rate.
Recent Trends:
In recent years, the USD to RUB exchange rate has witnessed fluctuations due to a combination of domestic and global factors. The imposition of sanctions on Russia, coupled with fluctuations in oil prices, has contributed to volatility in the RUB. Additionally, geopolitical tensions, such as the conflict in Ukraine and the strained relationship between Russia and Western countries, have influenced the exchange rate.
The Russian government’s economic policies, including efforts to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on oil exports, have also played a role in shaping the RUB’s value against the USD. The central bank’s interventions in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the currency have been notable in recent times.
Implications for Stakeholders:
- Importers and Exporters: Fluctuations in the USD to RUB exchange rate impact importers and exporters. A stronger RUB can make Russian exports more expensive, potentially affecting the competitiveness of Russian goods in international markets. On the other hand, a weaker RUB can benefit exporters but may increase the cost of imports.
- Investors: Investors, both domestic and foreign, closely monitor exchange rates as they influence the returns on investments. Changes in the USD to RUB rate can impact the value of foreign investments in Russia and affect investment decisions.
- Tourism: Exchange rate movements also affect tourism. A stronger RUB can make Russia an attractive destination for foreign tourists, while a weaker RUB may make outbound travel more affordable for Russians.
Conclusion:
The USD to RUB exchange rate is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect of the global financial landscape. Understanding the factors influencing this exchange rate is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers. As geopolitical tensions, economic policies, and global events continue to shape the economic landscape, the USD to RUB exchange rate will likely remain a key indicator of Russia’s economic health and its integration into the global economy. Staying informed about these factors is crucial for making informed decisions in the ever-changing world of international finance.